A research team led by Prof Zheng Ying in the Institute of Chinese Medical Sciences (ICMS) at the University of Macau (UM) has discovered the prolonged circulation and elimination mechanism of crosslinked polymeric micelles in zebrafish model, providing scientific support and guidance for the rational design and optimisation of injected nanomedicines. Their finding can help researchers improve the efficacy of nanomedicines and reduce toxic and side effects. The study has been published in Biomaterials, a top international journal in the field.
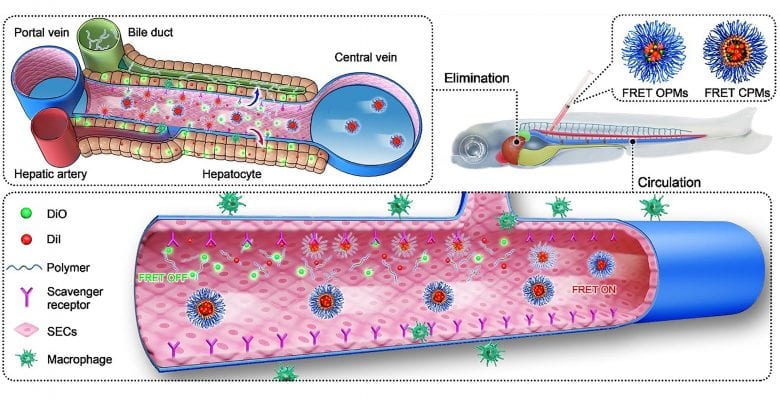
In recent years, a myriad of nanoparticle carrier systems (nanomedicines) has emerged, but few products have achieved successful clinical application. The main reason for this gap is the lack of understanding of the behaviour and biofate of nanomedicines in vivo. Because it is difficult for light (visible light and fluorescent light) to penetrate thick tissues, the in vivo tracking of nanomedicines in rodents is severely limited by the restricted imaging possibilities within these animals. To address this challenge, the team used FRET (fluorescence or Förster resonance energy transfer) imaging in combination with a visual zebrafish larvae model (7 dpf) to realise in vivo quantification and visualisation of intact polymeric micelles. Through this technique, they revealed the behaviour and elimination mechanism of polymeric micelles in vivo at both whole organism level and cellular molecular level.
The study found that endothelial cell scavenger receptors play a major role in mediating the capture of micelle nanoparticles in the zebrafish’s caudal vein and liver. After dissociation in vivo, the polymer micelles are quickly eliminated through the hepatobiliary pathway and excreted to the gastrointestinal tract, while it is difficult to eliminate the intact polymer micelles out of the body. The study can help researchers understand the delivery of nanomedicines in vivo and optimise the drug delivery system, thereby improving drug efficacy and reducing toxic and side effects.
The study is supported by Macao Science and Technology Development Fund (File Number: 0013/2018/A1) and UM’s research fund (File Number: MYRG2017-00200-ICMS). Tao Jinsong, a PhD student in the ICMS, is the first author of the study, and Zheng Ying is the corresponding author. Other individuals who have made important contributions to the study include UM master’s students Wei Zhengjie and Yan Xingyang, PhD student He Yuan, ICMS professor Lee Ming-Yuen, Faculty of Health Sciences professor Ge Wei, and Peking University School of Pharmaceutical Sciences professor Wang Xueqing.
The research article is available at https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0142961220304269?dgcid=rss_sd_all